Process engineering plays a pivotal role in industries such as chemical, oil and gas, petrochemical, and pharmaceuticals. It encompasses designing and optimizing processes that convert raw materials into valuable products.
As the backbone of a project, process engineers collaborate closely with various disciplines, including piping, instrumentation, and mechanical engineering. Their primary objective is to ensure the project adheres to safety, environmental standards, and profitability goals. You can check out this article to gain a deeper understanding of the role of a process engineer and their key responsibilities and explore their main activities.
In this article, we will focus on the critical first step in any project: plant simulation. By developing a comprehensive and optimized process simulation, process engineers significantly impact downstream process activities and subsequent engineering tasks. A proper process simulation results in an efficiently functioning plant that remarkably meets project objectives.
You can watch the content of the article in the below video. Otherwise you can skip and continue reading:
Role of Plant Simulation within a Project
Plant simulation allows process engineers to create a virtual representation of the plant process, thereby, we can figure out what we need to achieve the target of building the plant.
Through a proper process simulation, we can know what pieces of equipment are required, their expected inlet and outlet flow rates, or in other words, capacities, fluid compositions, physical properties, and the operating pressures and temperatures at each piece of equipment.
Knowing this information is essential for carrying out all the downstream activities. For example, when we know the flow rate and physical properties, we can begin sizing activities of equipment and piping. Through the fluid composition, we can know the material of construction of different process components.
Operating pressure and temperature are also essential to carry out hydraulic calculations and equipment selection. In addition, specifying the correct pressure and temperature ensures proper mechanical design and selection of equipment, piping, and instruments.
If the plant simulation isn’t carried out properly, this would severely affect all these activities, which means that all these activities should be revisited. Otherwise, this can lead to oversized or undersized plant components and even safety issues.
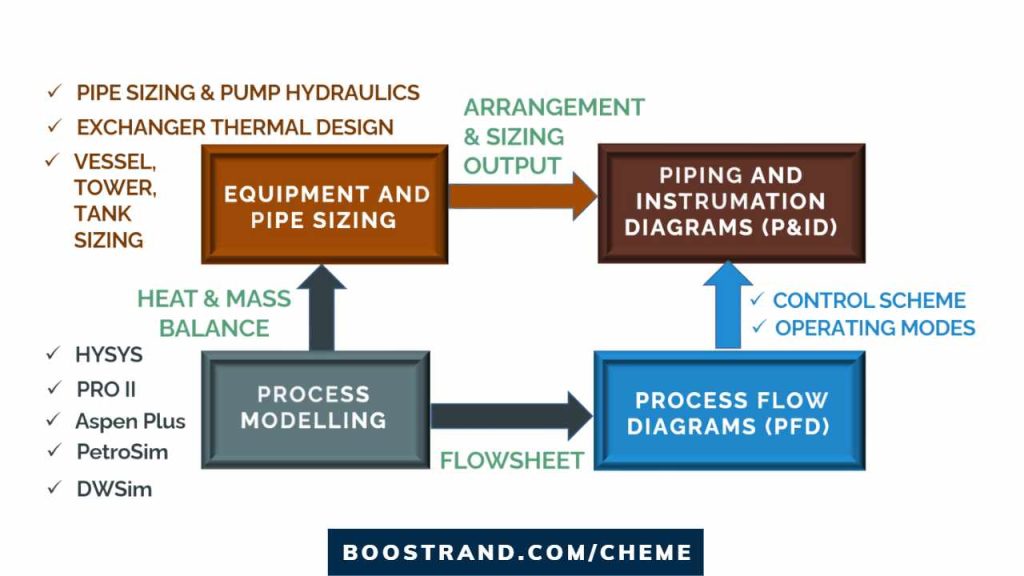
Common Process Simulation Software
Plant simulation is carried out using proven software dedicated to this task. Several process simulation software packages are available in the market, each with its unique set of features and capabilities. These software packages enable process engineers to develop comprehensive and accurate models of the plant and its processes.
Through a robust set of features and capabilities for both the design and optimization of steady-state processes, particularly those that involve complex reactions and separations. Efficient simulation software offers an extensive library of thermodynamic models and property estimation methods, which are essential for accurate process modeling.
Some of the most widely used modeling software tools include:
- Aspen Plus: mostly used for chemical industries
- HYSYS: mostly used in gas plants and in many other processes
- PROII: mostly used in refining processes
- And even others!
Process Engineering Masterclass
Become a Professional Process Engineer, discover process engineering career, role, activities and common practices with access to most of the courses here.
Factors to consider in process modeling and simulation
When carrying out process simulation, we must handle the input data with high care. This is because the data we input to our model will highly affect the output results. If we enter exaggerated or distorted data, this can lead to extreme conditions that are difficult to handle by equipment or lead to modes of operation that won’t occur in reality, which may lead to a plant that is sized based on false data. This can cause many issues such as undersized equipment, wrong materials of construction, an operation that cannot be achievable, ..etc.
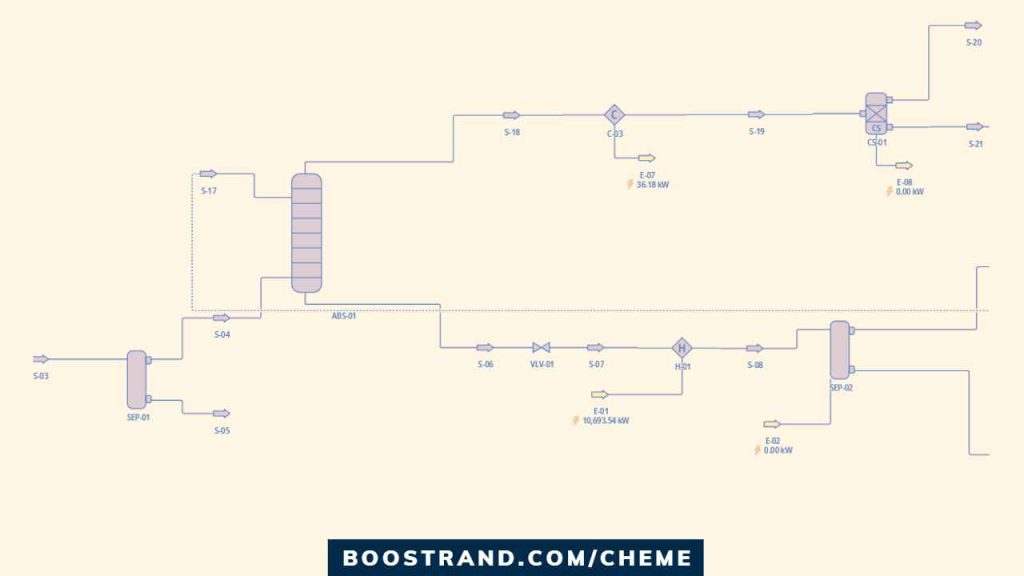
So let’s dive into the main input data to a process simulation software:
a. Feed composition and physical properties
The composition and physical properties of the feedstock play a crucial role in the accuracy of process models and simulations.
Examples:
- Ensuring accurate and up-to-date information on the feedstock’s composition.
- Impurities should be well recognized as they can affect the plant operation and may lead to adding new equipment to get rid of them.
- Proper fluid package relevant to the feed type should be well chosen. The fluid package shall affect the output physical properties such as density, viscosity, and thermal conductivity. This shall highly affect the sizing and type selection of equipment, instruments, and piping.
b. Product specifications
Product specifications are another important factor when developing process models and simulations. These specifications define the desired quality and properties of the final product, and process engineers must ensure that the process is designed and operated in a way that meets these requirements.
Examples:
- A product purity of 95% may lead to much simpler tower configuration than a target priority of 99%.
- Or if we want a target pressure at the battery limit of the plant to a downstream facility of 20 barg. This can lead to more compression stages than a target pressure of 15 barg, for example, which means more compressor coolers and receivers. In our compressors course, we talked about how discharge temperature affects the operation of a compressor.
By incorporating product specifications into the process models and simulations, process engineers can evaluate the impact of various process alternatives on the final product and select the best option.
c. Available Utilities
The availability and cost of utilities such as electricity, water, and steam can significantly impact the design and operation of the plant. Process engineers must consider these factors when developing the plant model, as they can influence the selection of equipment, operating conditions, and overall plant performance. By considering available utilities, process engineers can optimize the plant’s energy consumption and minimize operating costs, while ensuring that the plant meets its production requirements. This would even be more clear when starting to prepare utility consumption.
Process Engineering Masterclass
Become a Professional Process Engineer, discover process engineering career, role, activities and common practices with access to most of the courses here.
Example:
- Steam availability, so if we need to heat a fluid, is there steam available to use? If it is not available, shall we consider a new steam system to heat our fluid? Or we would need to look for another alternative, such as hot oil or electric heating for example?
d. Ambient conditions
Ambient conditions, mainly temperature, can also impact the performance of the plant and its equipment. Another famous example here can be the
Example:
- Use of air cooled exchanger: If we need to cool a fluid, shall we cool it by air or by water or by both? If there is enough temperature difference between the air temperature and the target temperature we want to reach, then we may think about an air cooler. I have made an article about when to use an air cooled exchanger versus a water cooler, you can check it out if you like.
Simulation Software Main Output
So what are we expecting from a process simulation? Process simulation software packages generate several essential outputs, let’s check them out:
a. Process Flow Sheet
The process flow sheet is a graphical representation of the plant and its processes, illustrating the flow of materials and energy through the various unit operations. Through the flow sheet, we can see the equipment we need, and the purpose of each one. We can also have a preliminary process scheme that shall be the base of the Process Flow Diagram (PFD).
b. Heat and Mass Balance
Heat and mass balance is a fundamental output of process simulation software, providing a detailed account of the flow of materials and energy throughout the plant. Through the Heat and Material Balance (HMB) Table, we know each process stream’s expected flow rate and operating conditions. We can use this data to carry out sizing activities of piping, check plant hydraulics, and specify instrument process data.
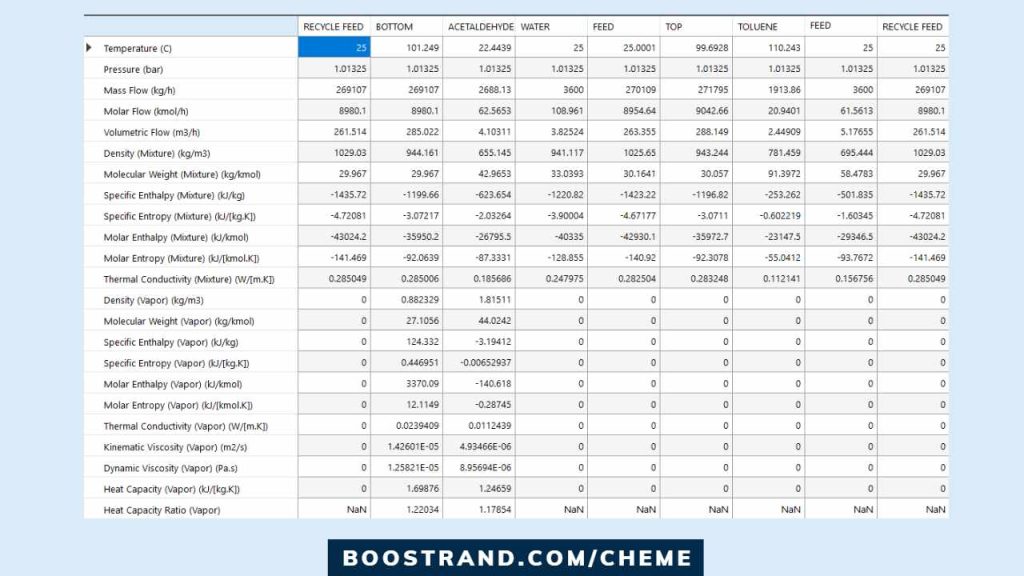
c. Equipment Design Parameters (e.g. exchanger duty, tower tray profiles, inlet and outlet streams, etc.)
The equipment design parameters are another essential output of process simulation software, providing detailed information on the design, operation, and performance of various equipment within the plant.
Examples:
- exchanger duty, inlet and outlet temperatures that are needed for thermal design.
- tower tray profiles that are needed for tower sizing
- inlet and outlet streams that are needed for pipe sizing, pump, and control valve hydraulics
- Compressor scheme and operating parameters
- and even more.
By analyzing this data, process engineers can optimize equipment design and selection of main type and internals, ensuring that each piece of equipment shall achieve its function in harmony with other plant components.
Process Engineering Masterclass
Become a Professional Process Engineer, discover process engineering career, role, activities and common practices with access to most of the courses here.
d. Identifying Operating Cases / Scenarios
When carrying out process simulation, a process engineer should consider all the plant’s expected operating scenarios (also known as cases). For example, feed temperature may be higher in summer than in winter. This can affect lots of factors that shall impact downstream activities.
Examples:
- Maybe we fear very high viscosity or reaching the fluid pour point. This can drastically affect pump selection, pipe sizing, heat transfer equipment, …etc.
- In summer, air and water coolers will perform worse than in winter, and so on.
- Fluid compositions: The feed gas contains more light ends in some cases than in other operating cases. This can highly affect the capacity of the tower overhead system, compressor capacities, …etc.
So here, a process engineer should be aware of all expected scenarios to ensure that all downstream activities are carried out on a solid basis.
Next step: Creating process flow diagrams (PFDs)
Process flow diagrams (PFDs) are graphical representations of the process flow sheet, illustrating the flow of materials and energy through the various unit operations. PFDs are an essential tool for process engineers, as they visually represent the whole process.
The creation of PFDs is a critical step in the project, especially during early project phases, as it enables process engineers to communicate the process design and operation to other engineering disciplines and stakeholders, such as operators, maintenance personnel, and management. PFDs also serve as a basis for developing piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), which provide a detailed representation of the plant’s equipment and instrumentation, based on which other discipline activities are carried out.
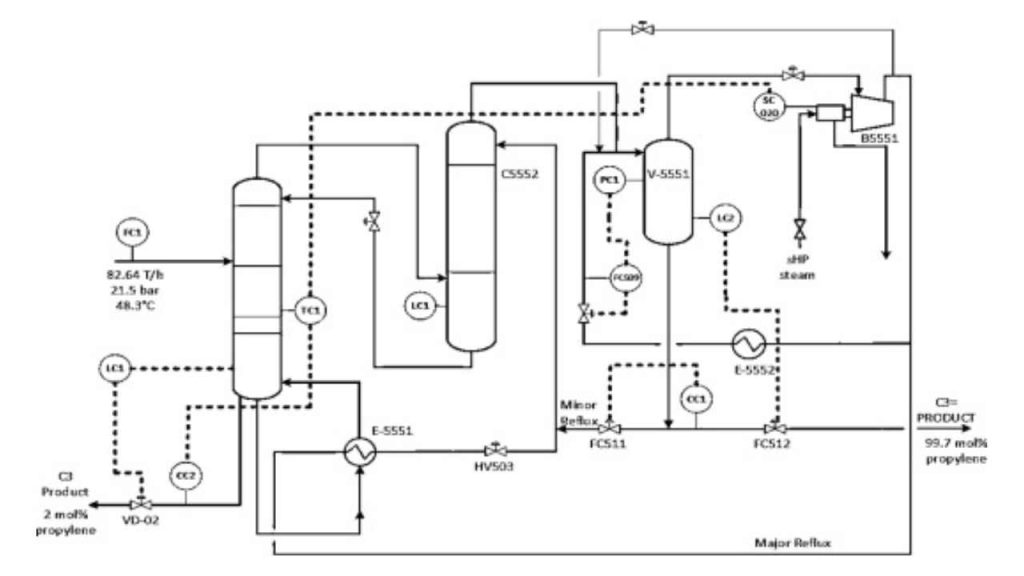
Conclusion
Plant simulation is an indispensable activity carried out by a process engineer, offering numerous benefits such as reducing the time and cost associated with process development and optimization. Common process simulation software packages such as Aspen Plus, PROII, and HYSYS provide process engineers with comprehensive and accurate models of the plant and its processes, which serve as the foundation for a successful project.
Process modeling and simulation require process engineers to consider several factors, such as feed composition and physical properties, product specifications, available utilities, and ambient conditions. By accounting for these factors, process engineers can develop accurate and reliable process models and simulations that reflect the real-world operating conditions of the plant. The creation of PFDs is a critical step in the process modeling and simulation process, providing a visual representation of the process design and operation and a basis for P&ID development.
Overall, the role of process engineers in process modeling and simulation is critical, enabling the successful design, optimization, and operation of processes that produce valuable products while minimizing costs and energy consumption.
Start your Career
Access Process Engineering Introduction Course
Share this:
[…] creation of a PFD is typically based on the output of process simulation software. We have discussed plant simulation’s role in a project in the previous article. In a nutshell, process simulation involves using specialized software to model and analyze the […]